In a significant development, Chinese authorities have allowed all domestic companies to import Australian coal, thereby putting an end to ‘informal’ trade restrictions imposed in late 2020. Ports and customs offices have been told to allow Australian coal cargoes.
Earlier this year, the authorities had given four State-owned companies permission to resume purchases of Australian coal. Of the four, State-owned Baowu Group was the lone steel producer, while the rest were power companies.
It is believed that more than 1 million tonnes (mnt) of Australian coal cargoes are set for Chinese shores in March. Due to the rise in global coal prices after Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, the price difference between China’s domestic coal and Australian coal had substantially decreased. As a result, the withdrawal of the ‘unofficial’ ban on Australian coal will bring marginal economic benefit to China.
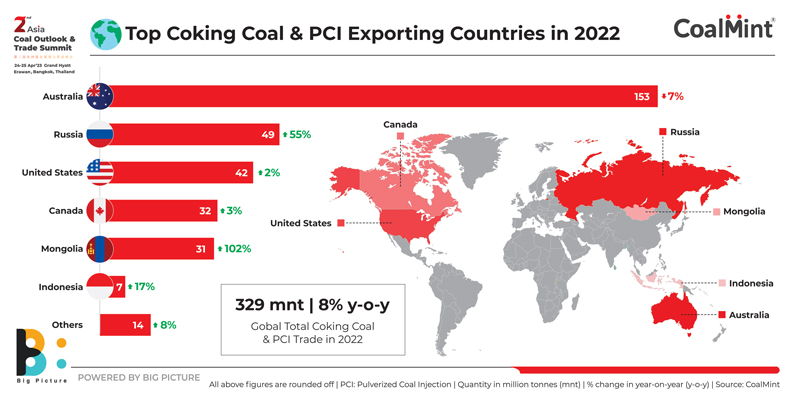
Imports from Australia
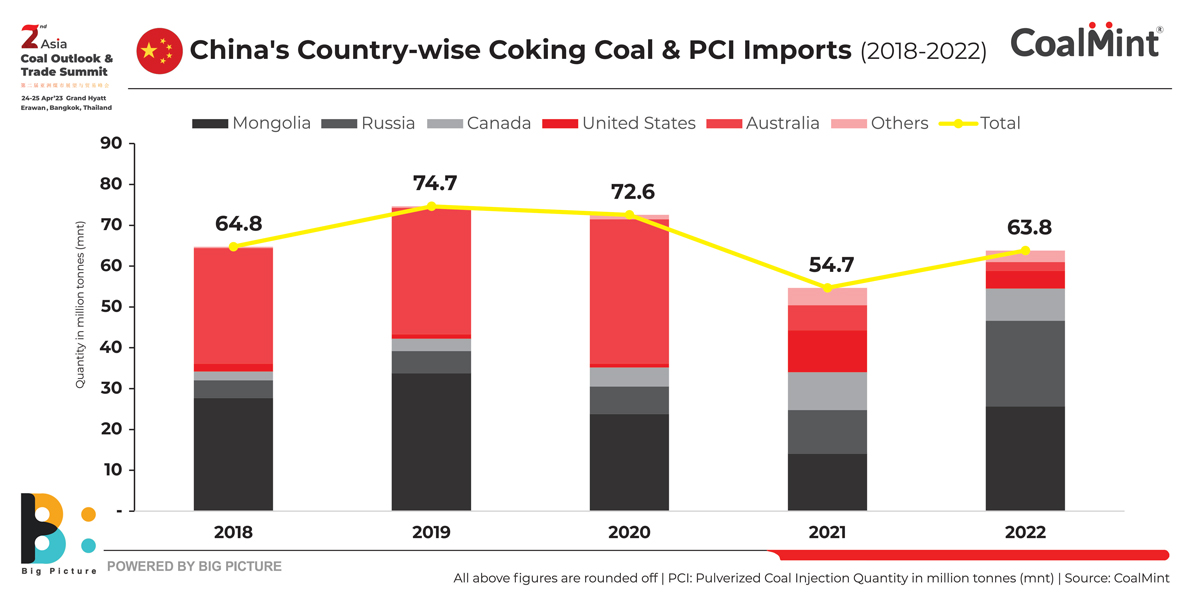
CoalMint data reveal that China’s imports of non-coking coal from Australia, mainly high-energy coal, decreased by about 90% in 2021 from 2020. China’s imports fell to 5.5 mnt from over 42 mnt in the previous year. Imports were recorded at zero in 2022.
As regards coking coal, China’s imports from Australia declined sharply by over 80% y-o-y in 2021 to just about 6 mnt compared with more than 35 mnt in 2020.
However, volumes are sure to surge after China’s move to resume imports. The decision to resume coal imports from Australia is partly driven by the need to tame domestic coal prices amid global volatility.
But China’s coal imports from Mongolia and Russia increased significantly on-year in 2022, as Covid restrictions were slowly eased along the China-Mongolia border allowing for free vehicular movement, as well as cheap Russian coal offers amid global energy inflation.
Impact on coking coal market
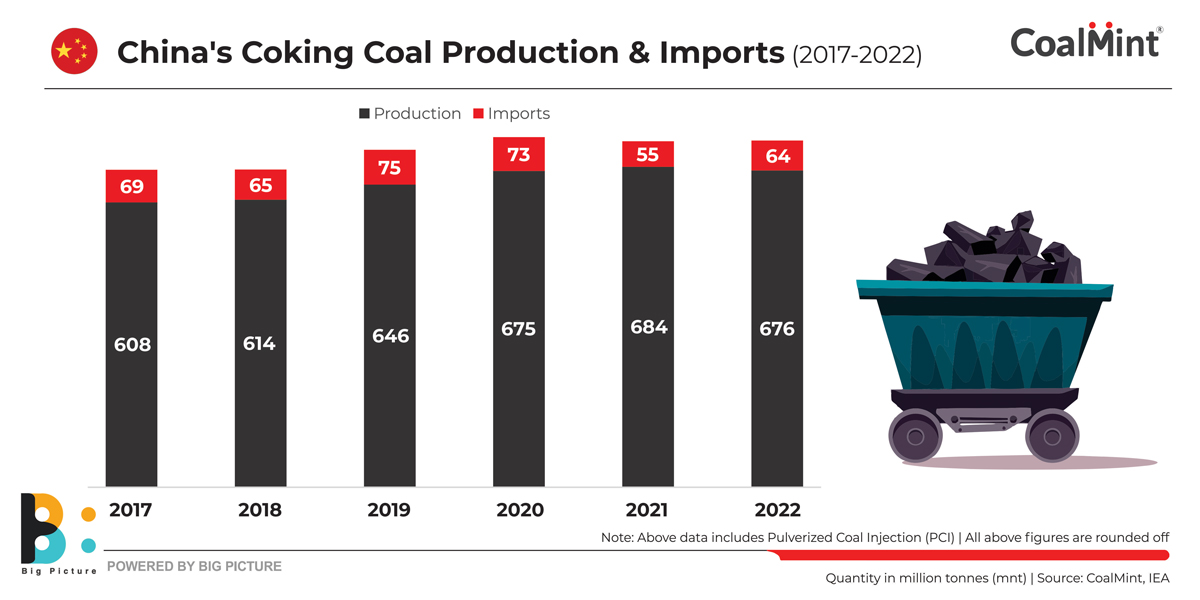
Sources believe that with the full reopening of Australian coals into China, the increase in supply of seaborne imported material will exert some downward pressure on the coking coal market. China’s domestic raw coal production in Jan-Feb’23 also increased by around 6% y-o-y to 735 mnt, as per NBS data.
In fact, coking coal and coke futures on China’s Dalian Commodity Exchange (DCE) edged down after news came in of permission being granted to all Chinese companies to resume Australian coal purchases. FOB Australian prices of premium low-volatile coking coal are still higher than CFR China prices by around $6-10/t. In the CFR China market, prices inched lower on weaker sentiments, with the DCE futures market observing May coking coal and coke contracts dropping by 4.53% and 3.04% yesterday.
Outlook
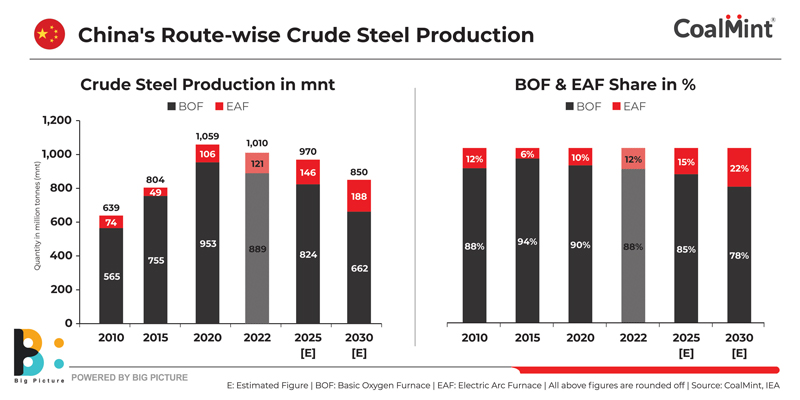
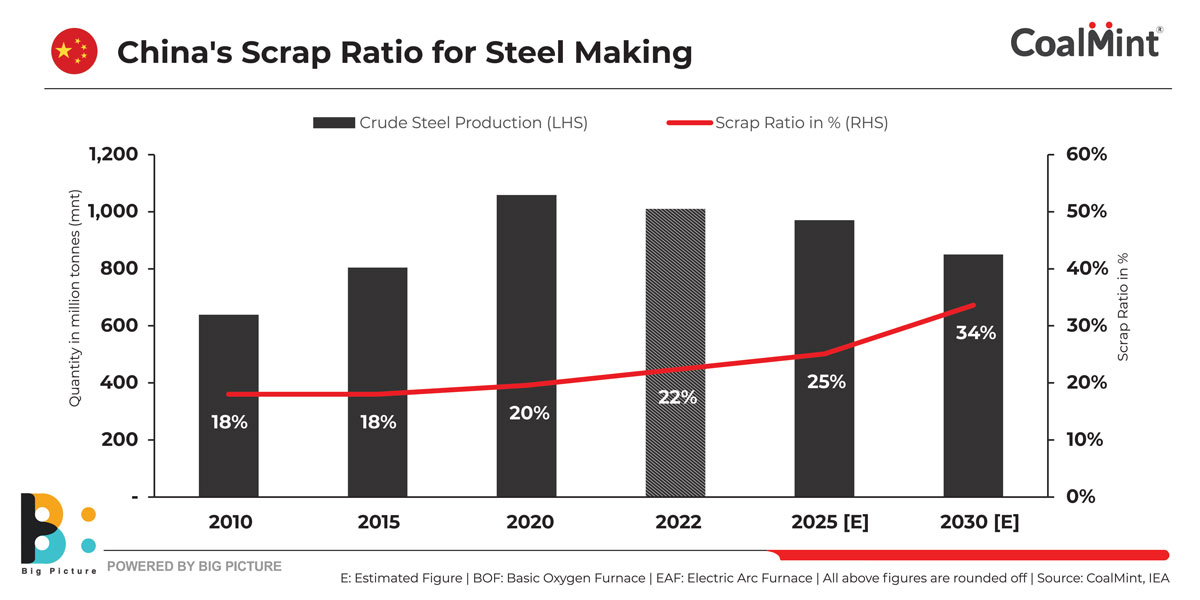
Domestic met coal production in China is set to face hurdles going forward as environmental restrictions push authorities to clamp down on mining activities in coal-rich provinces. At the same time, high steel industry capacity utilisation at times may drive met coke imports from SE Asian countries with surplus capacities.
Demand for Australian high-energy Newcastle coal may remain rangebound in the near term even though new domestic coal mining capacity is approved.
In the short term, however, Australian premium low-volatile hard coking coal may continue to attract buying interest, despite competitive offers from Russia, even as uncertainties persist over pricing and logistics from Mongolia.
CoalMint’s 2nd Asia Coal Outlook & Trade Summit
China’s coking coal imports increased by over 15% on the year in 2022. Will imports increase in 2023, too, with the resumption in inflow of Australian cargoes? Would Chinese buyers have appetite for Australian thermal coal given other low-priced alternatives?
Follow the discussion at CoalMint’s 2nd Asia Coal Outlook & Trade Summit to be held at the Grand Hyatt Erawan, Bangkok, Thailand on 24-25 April, 2023, where Mr. Jiyuan Wang, Marketing Manager, Shaangu Group from China, will share his insights.