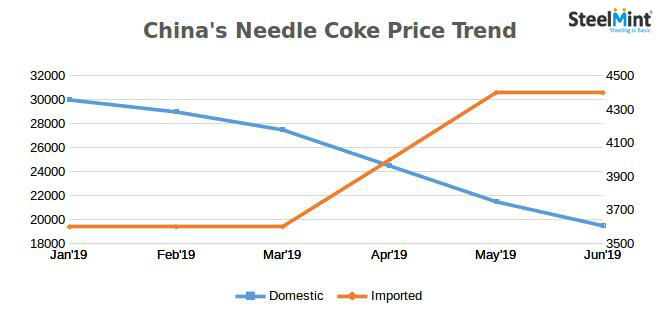
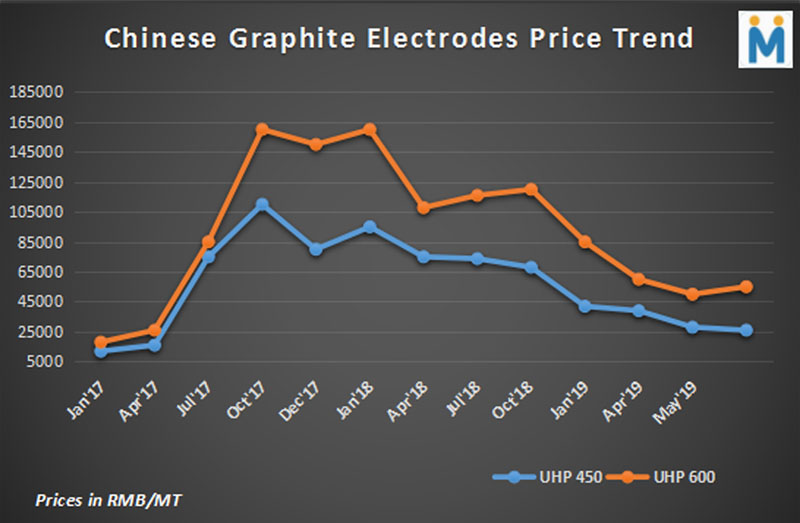
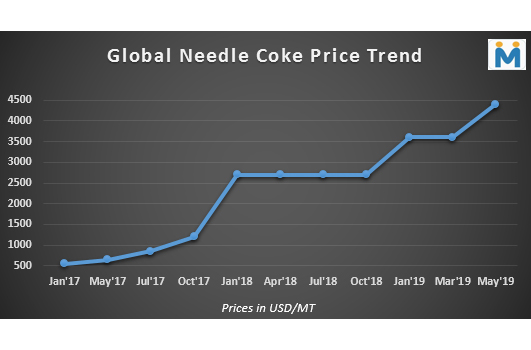
IMO 2020 is likely to exert pressure on the main consumers of needle coke – the GE and lithium-ion battery industries
At a time when it seemed that the panic in the global Graphite Electrode (GE) industry had subsided and prices had returned to normal levels almost after two years, with supplies from China witnessing a dramatic surge, another surprise might just be in the offing. This is the new IMO 2020 regulations to be implemented from 1 January, 2020 which are expected to have a tangible effect on needle coke supplies and prices.
What are the IMO 2020 regulations?
From 2020 the International Maritime Organization (IMO) will require ships to reduce their emissions to be equivalent to use marine fuels with a maximum sulphur content of 0.5%, far lower than the current 3.5%. This new measure requires the maritime industry to comply but the shipping industry is not yet ready to deal with this regulation.
This stringent sulphur regulation has led ship owners and operators to mull all available options they have in order to comply with the IMO regulation, and refiners are considering producing more low-sulphur fuel to meet possibly higher demand, as both parties anticipate an unprecedented change in the marine fuels supply seascape.
Industry experts believe that given the limited time left and with the shipping industry being unprepared, there are three options for those forced to comply with the new regulation: first, ship owners can install exhaust gas cleaning systems on their ships. Second, ships can run on clean LNG gas as fuel, Third, they can buy compliant fuels at higher costs.
The installation of exhaust gas cleaning system will definitely lead to increase in costs for the ship owners and operators further resulting in higher freight charges whereas the option of switching to cleaner gas is not easy at all. In case of last option, the refineries have been reluctant to undergo large capital investments required for the major upgrades to increase production of low sulphur marine fuel oils.
How will the regulation affect needle coke prices?
Needle coke – an already scarce product – is a key raw material in GE production, which is used both in EAF steel-making and manufacturing of synthetic graphite used as anode material for lithium ion batteries that power electric vehicles.
There are two types of needle coke – petroleum needle coke produced at oil refineries by converting decant or slurry oil along with high quality vacuum residue (both by-products of the refining process) and coal-based needle coke (sometimes called ‘pitch needle coke’, or just ‘pitch coke’) made from coal tar pitch, a by-product of coking metallurgical coal in BF steel-making.
There are only 10 needle coke manufacturers in the world, with the majority of them producing petroleum needle coke. Out of the 10, seven operate outside China with Phillips 66 (US and UK) being the largest, followed by Seadrift in the US and C-Chem, Petrocokes, JX Nippon and Mitsubishi in Japan. Indeed, ex-China capacity has remained broadly flat over the past 10 years given the high capital costs, technical expertise and stringent regulatory processes required to set up a greenfield needle coke project. In contrast, China is not only a net importer of needle coke but also a large producer, primarily through the coal-based route, with Sinosteel being the largest.
Supply side structural changes in China in the last two years have resulted in the promotion of EAFs thereby boosting GE demand and consequently needle coke requirements and prices.
Under the new IMO rules, the price of low-sulphur crude oil required to produce needle coke is expected to rise as more of it will be diverted toward marine fuels. Needle coke producers would be forced to contend with either increased competition for feedstock or investments in equipment to allow use of high-sulphur oil. Either way, IMO 2020 is likely to exert pressure on the main consumers of needle coke – the GE and lithium-ion battery industries.
How trade dynamics may change
Despite rise in demand, no major greenfield or brownfield needle coke projects have been announced outside China over the past few years given the high capital investment as well as technical challenges involved.
In the case of China, although many steel companies and GE manufacturers have invested in needle coke units due to sudden spurt in demand, a majority of them are coal-tar pitch based projects and environmental concerns will limit supply of coal-tar pitch especially during the winter heating season in a bid to maintain air quality. In case of the handful of petroleum-based projects, the two major challenges are lack of technical knowhow and sourcing of good quality feedstock (low-sulphur crudes) the supply of which is already limited.
Subsequently, the strong demand from steelmakers and the lithium-ion battery segment as well as the enforcement of the IMO 2020 restrictions will eventually tighten the supply of needle coke from next year onwards thereby adversely affecting prices.

Know More